Learn More
Invitrogen™ Actin (muscle) Monoclonal Antibody (HHF35), Alexa Fluor™ 488, eBioscience™
Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
Supplier: Invitrogen™ 53649682
Description
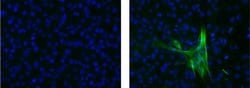
Description: The monoclonal antibody HHF35 recognizes muscle actin; specifically the alpha and gamma form found in skeletal cardiac, and smooth muscle. No reactivity to the beta form is observed. The 42 kDa protein is a main component of the cytoskeletal structural network. The HHF35 antibody has been shown to recognize actin from smooth muscle cells of the heart, bladder, uterus, gastrointestinal tract, and diaphragm. The antibody stains tumors of muscle origin such as leiomyomas, leiosarcomes and rhabdomyosacromas. The HHF35 antibody recognizes human, mouse, rat, bovine, canine and non-human primate actin. Applications Reported: This HHF35 antibody has been reported for use in immunohistochemical staining of frozen tissue sections, immunohistochemical staining of formalin-fixed paraffin embedded tissue sections, and immunocytochemistry. Applications Tested: This HHF35 antibody has been tested by immunocytochemistry and can be used at less than or equal to 30 μg/mL. It is recommended that the antibody be carefully titrated for optimal performance in the assay of interest. Excitation: 488 nm; Emission: 519 nm; Laser: Blue Laser. Filtration: 0.2 μm post-manufacturing filtered.
The product encoded by this gene belongs to the actin family of proteins, which are highly conserved proteins that play a role in cell motility, structure and integrity. Alpha, beta and gamma actin isoforms have been identified, with alpha actins being a major constituent of the contractile apparatus, while beta and gamma actins are involved in the regulation of cell motility. This actin is an alpha actin that is found in skeletal muscle. Mutations in this gene cause nemaline myopathy type 3, congenital myopathy with excess of thin myofilaments, congenital myopathy with cores, and congenital myopathy with fiber-type disproportion, diseases that lead to muscle fiber defects.Specifications
| Actin (muscle) | |
| Monoclonal | |
| 0.5 mg/mL | |
| PBS with 0.09% sodium azide; pH 7.2 | |
| P62736, P62737, P62738, P62739, P63258, P63259, P63260, P63261, P63267, P63268, P63269, P68032, P68033, P68035, P68133, P68134, P68136, P68137, P68138, Q3ZC07, Q5E9B5 | |
| ACTA1, ACTA2, ACTC1, ACTG1, ACTG2 | |
| Affinity chromatography | |
| RUO | |
| 100050139, 100057561, 100057678, 100062175, 100065454, 100152267, 100154254, 100520667, 100716255, 100716933, 100722917, 100731713, 100731953, 11459, 11464, 11465, 11468, 11475, 25365, 281592, 281595, 287876, 29275, 29437, 397653, 404122, 475792, 475923, 477587, 478250, 488984, 515610, 533219, 58, 59, 70, 71, 72, 733615, 81633 | |
| 4°C, store in dark, DO NOT FREEZE! | |
| Liquid |
| Immunohistochemistry (Frozen), Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin), Immunocytochemistry | |
| HHF35 | |
| Alexa Fluor 488 | |
| ACTA1 | |
| 0610041G09Rik; AA959943; a-actin; AAT6; ACT; Act4; ACT-4; ACTA; ACTA1; ACTA1 protein; Acta2; Acta-2; ACTA3; ACTB; Actc; ACTC1; Actc-1; ACTE; Actg; Actg1; Actg2; ACTGE; actin; actin alpha 1; actin alpha 1, skeletal muscle; actin alpha 2, smooth muscle; actin alpha cardiac; actin alpha cardiac 1; actin alpha cardiac muscle 1; actin gamma 1; actin gamma 2, smooth muscle; actin homolog; actin, alpha 1, skeletal muscle; actin, alpha 2, smooth muscle, aorta; actin, alpha cardiac muscle 1; Actin, alpha cardiac muscle 1, intermediate form; Actin, alpha skeletal muscle; Actin, alpha skeletal muscle, intermediate form; actin, alpha, cardiac 1; actin, alpha, cardiac muscle; actin, alpha, cardiac muscle 1; actin, alpha, vascular smooth muscle; actin, aortic smooth muscle; Actin, aortic smooth muscle, intermediate form; actin, beta; actin, cytoplasmic 2; Actin, cytoplasmic 2, N-terminally processed; Actin, cytoplasmic type 5; actin, cytoplasmic, type 5; actin, gamma 1; actin, gamma 1 propeptide; actin, gamma 2; actin, gamma 2, smooth muscle, enteric; actin, gamma, cytoplasmic 1; actin, gamma-enteric smooth muscle; Actin, gamma-enteric smooth muscle, intermediate form; actin-like protein; Actl; ACTL3; Acts; ACTSA; Actsg; Actsk-1; Actvs; AL023024; alpha actin; alpha actin 1; alpha actin 2; alpha-actin; alpha-actin cardiac; alpha-actin-1; Alpha-actin-2; alpha-actin-3; alphac-actin; Alpha-cardiac actin; alphaSMA; alpha-sma; alpha-smooth muscle actin; ASD5; ASMA; a-SMA; B-actin; beta actin; beta-actin; beta-actin FE-3; BRWS2; cardiac actin; cardiac alpha actin; cardiac muscle alpha actin 1; cell growth-inhibiting gene 46 protein; CFTD; CFTD1; CFTDM; CMD1R; CMH11; cytoplasmic 2; cytoplasmic actin; cytoplasmic beta-actin; cytoplasmic type 5; cytoskeletal gamma-actin; deafness, autosomal dominant 20; deafness, autosomal dominant 26; DFNA20; DFNA26; E51; epididymis luminal protein 176; gamma 1 propeptide; gamma-2-actin; Gamma-actin; gamma-enteric smooth muscle actin; GIG46; HEL-176; hypothetical protein LOC515610; LOW QUALITY PROTEIN: actin, alpha skeletal muscle; LVNC4; MPFD; MYMY5; NEM1; NEM2; NEM3; nemaline myopathy type 3; RP5-1068B5.2; SHPM; similar to b-actin; skeletal alpha actin; skeletal muscle alpha-actin 1; SMalphaA; SMGA; smooth muscle alpha-actin; smooth muscle gamma-actin; type 5; unnamed protein product; vascular smooth muscle alpha-actin; VSCM | |
| Mouse | |
| 100 μg | |
| Primary | |
| Human, Mouse, Rat, Canine, Monkey, Bovine, Pig, Horse, Guinea Pig | |
| Antibody | |
| IgG1 κ |