Learn More
Invitrogen™ CD22 Monoclonal Antibody (eBio4KB128 (4KB128)), NovaFluor™ Yellow 755, eBioscience™
Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
Supplier: Invitrogen™ H053T03Y08A
Description
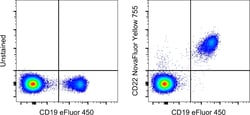
Description: The eBio4KB128 monoclonal antibody recognizes human CD22 (Siglec-2), which is a member of the siglec subgroup of the Ig superfamily. This product contains 1 vial of NovaFluor conjugate and 1 vial of CellBlox Plus Blocking Buffer. Applications Tested: This eBio4KB128 (4KB128) antibody has been pre-titrated and tested by flow cytometric analysis of normal human peripheral blood cells. This can be used at 5 μL (0.2 μg) per test. A test is defined as the amount (μg) of antibody that will stain a cell sample in a final volume of 100 μL. Cell number should be determined empirically but can range from 10^5 to 10^8 cells/test Master mixes. Whole Blood compatibility: When utilizing whole blood (as opposed to density-gradient-purified PBMC), we recommend lysing red blood cells in bulk prior to staining with NovaFluor conjugates
CD22, also known as BL-CAM, is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein composed of two polypeptide chains, CD22alpha and CD22beta, with molecular weights of 130 and 140 kDa, respectively. These chains are produced by alternative splicing of the CD22 gene. CD22 is prominently expressed on mature B cells and B cell lymphomas, including hairy cell leukemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, and nodular lymphocyte predominance Hodgkin's lymphoma, but is negative in classical Hodgkin's lymphoma. The extracellular portion of CD22 contains seven Ig-like domains that preferentially bind alpha2,6-linked sialic acid moieties found on epithelial, endothelial, B, and T cells. This binding can be masked by cis interactions with sialic acids on the same cell surface. CD22 expression is limited to late stages of B-cell differentiation, making it useful for phenotyping mature leukemias. Intracellularly, CD22 features six tyrosine residues within immunotyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIM) and activation-like motifs. These residues are phosphorylated upon B-cell receptor engagement, allowing CD22 to regulate B-cell receptor signaling. CD22 participates in positive regulation through interactions with Src family tyrosine kinases and acts as an inhibitory receptor by recruiting cytoplasmic phosphatases via SH2 domains, which block signal transduction through dephosphorylation of signaling molecules. CD22's role in both positive and negative regulation of B-cell signaling, along with its specific expression pattern, makes it a valuable marker for antibody customers interested in B-cell-related research and diagnostics.Specifications
| CD22 | |
| Monoclonal | |
| 0.2 μg/Test | |
| PBS with BSA and 0.09% sodium azide; pH 7.2 | |
| P20273 | |
| CD22 | |
| Affinity chromatography | |
| RUO | |
| 933 | |
| 4°C, store in dark, DO NOT FREEZE! | |
| Liquid |
| Flow Cytometry | |
| eBio4KB128 (4KB128) | |
| NovaFluor Yellow 755 | |
| CD22 | |
| A530093D23; B-cell receptor CD22; BL-CAM; B-lymphocyte cell adhesion molecule; B-lymphocyte cell adhesion molecule (BL-CAM); Cd22; CD22 antigen; CD22 molecule; FLJ22814; Lectin 2; Leu-14; Lyb8; Lyb-8; MGC130020; sialic acid binding Ig-like lectin 2; sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin 2; Sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin 2 (Siglec-2); Siglec2; Siglec-2; T-cell surface antigen Leu-14 | |
| Mouse | |
| 100 Tests | |
| Primary | |
| Human | |
| Antibody | |
| IgG1 κ |