missing translation for 'onlineSavingsMsg'
Learn More
Learn More
Invitrogen™ CD19 Recombinant Rat Monoclonal Antibody (6OMP31)
Rat Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
$639.17 - $1120.94
Specifications
| Antigen | CD19 |
|---|---|
| Clone | 6OMP31 |
| Concentration | 1 mg/mL |
| Content And Storage | -20°C, Avoid Freeze/Thaw Cycles |
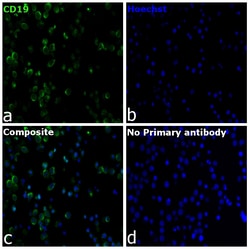
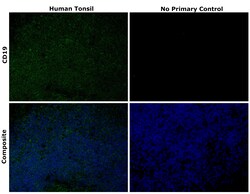
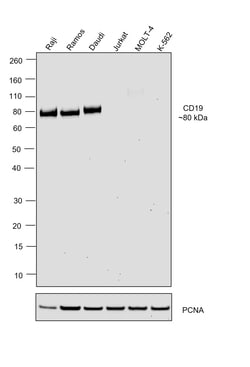
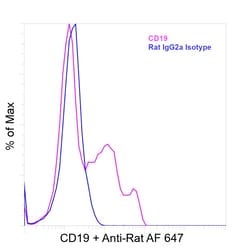
| Applications | Flow Cytometry, Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin), Western Blot, Immunocytochemistry |
Description
Recombinant rat monoclonal antibodies are produced using in vitro expression systems. Recombinant antibodies are produced using specific genes that code for the desired antibodies. These genes are cloned into an expression vector and expressed in vitro. The advantages of recombinant antibodies include better specificity and lot-to-lot consistency. It is recommended that the antibody be carefully titrated for optimal performance in the assay of interest.
CD19 is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, characterized by two Ig-like domains, and is expressed on B cells throughout all stages of development, excluding terminally differentiated plasma cells. It is also expressed on follicular dendritic cells and has been observed on myeloid leukemia cells, particularly those of monocytic lineage. CD19 is considered the earliest and broadest B cell-restricted antigen, and its expression is found in all B cell precursor leukemias. CD19 forms a multimolecular complex with CD21, CD81, Leu13, MHC class II, and the B cell receptor (BCR), playing a crucial role in B cell signaling. As a signal-amplifying coreceptor for the BCR, CD19 lowers the threshold for antigen receptor-dependent stimulation, allowing B cells to respond specifically and sensitively to various antigens through low-affinity antigen receptors. Signaling through CD19 induces tyrosine phosphorylation, calcium flux, and proliferation of B cells. Beyond its role as a BCR coreceptor, CD19 can also signal independently of BCR co-ligation, serving as a central regulatory component upon which multiple signaling pathways converge. This makes CD19 an important functional regulator of both normal and malignant B cell proliferation. Mutations in the CD19 gene can result in hypogammaglobulinemia, a condition characterized by low levels of immunoglobulins, while CD19 overexpression can lead to B cell hyperactivity. CD19 is expressed on 100% of peripheral B cells, as defined by the expression of kappa or lambda light chains, underscoring its significance in B cell function and immune regulation.Specifications
| CD19 | |
| 1 mg/mL | |
| Flow Cytometry, Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin), Western Blot, Immunocytochemistry | |
| Unconjugated | |
| Rat | |
| RUO | |
| PBS with 0.09% sodium azide; pH 7.4 | |
| P15391 | |
| 930 | |
| Primary | |
| Affinity chromatography |
| 6OMP31 | |
| -20°C, Avoid Freeze/Thaw Cycles | |
| Recombinant Monoclonal | |
| Liquid | |
| IgG2a κ | |
| Human | |
| Cd19 | |
| AW495831; B4; B-lymphocyte antigen CD19; B-lymphocyte surface antigen B4; Cd19; CD19 antigen; CD19 molecule; CVID3; differentiation antigen CD19; Leu-12; T-cell surface antigen Leu-12 | |
| Cd19 | |
| Antibody |